Theory of demand
Question 1
What is Demand?
Ans: Demand is an economic principle that refers to the consumers’ desire to purchase goods and services and their willingness to pay a particular price for those goods and services.
Question 2
What are the Determinants of Demand?
Ans: The Determinants of Demands are:
- Price of the given commodity
- Price of related goods
- The income of the customer
- Tastes and preferences
- The expectation of change in the price in future
Question 3
What is the demand function?
Ans: Demand function shows the relationship between quantity demanded a particular commodity and the factors influencing it.
Question 4
Define the law of demand.
Ans: The law of demand states the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded, keeping other factors constant (ceteris paribus).
Question 5
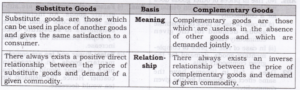
What are Complementary goods?
Ans: Complementary goods are those goods that are used together to satisfy a particular want.
Question 6
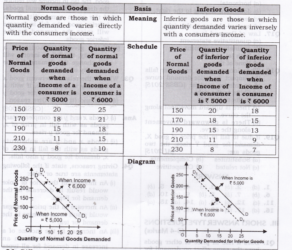
Define Normal goods.
Ans: Normal goods are referred to as those goods that witness an increased demand corresponding to rise in income of consumers. The demand for normal goods is determined by the state of income of the consumer. If consumer income increases, demand increases and if income decreases, demand also declines.
Question 7
What are Inferior Goods?
Ans: Inferior goods refer to those goods whose demand decreases with an increase in income. And, this is known as Inferior goods.
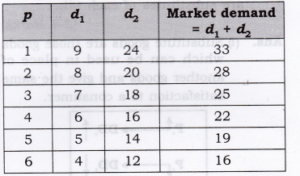
Question 1. Suppose there are two consumers in the market for a good and their demand functions are as follows: D1(p)=20−P for any price than less 20, and D1(p)=0 at any price greter than or equal to 20. D2(p)=30−2P for any price less than 15 and D2(p)=0 at any price greater than or equal to 15. Find out the market demand function.
Answer: It can be seen from the given demand functions that Consumer 1 do not want to demand the goods for any price greater than or equal Rs.20 and consumer 2 do not want to demand the goods for any price greater than Rs 15.
Hence, the market demand function will be,
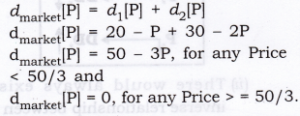
Question 3.
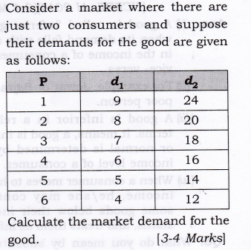
Answer:
Question 4. What do you mean by a normal good?(or)
when good is called ‘normal goods’?
Answer: for normal good, with a raise in income,the demand of the commodity also rises and vice versa. Shortely direct relationship exists the income of a coustomer and demand of normal good.For example, a new car, new clothings.
Question 5. What do you mean by an ‘inferior good’? Give some examples.
Or
Give the meaning of inferior good and explain the same with the help of an example.
Answer:
1. A good is called ‘inferior goods’ when its demand falls with a rise in the income of a consumer and vice- versa.
2. For example, Jowar or Bajra for a poor person.
3. A good is inferior in a relative terms. It means, a good is inferior or normal is determined by the income level of a consumer.
4. When a consumer moves to higher income, he/she may consider some goods below their income status, and treats them as inferior.
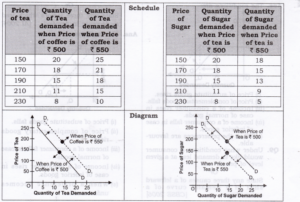
Question 6. What do you mean by substitutes? Give examples of two goods which are substitutes of each other.
Answer:
1. Substitute goods are those goods which can be used in place of another goods and give the same satisfaction to a consumer.
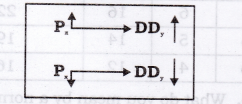
2. There would always exist a direct relationship between the price of substitute goods and demand for given commodity.
3. It means with an increase in price of substitute goods, the demand for given commodity also rises and vice-versa.
4. For example, Pepsi and Coke, tea and coffee are substitute to each other.
Question 7. What do you mean by complements?
Give examples of two goods which are complements of each other.
Answer:
1. Complementary goods are those which are useless in the absence of other goods and which are demanded jointly.
2. There would always exist an inverse relationship between price of complementary goods and demand for given commodity.
3. It means, with a rise in price of complementary goods, the demand for given commodity falls and vice-versa.
4. For example pen and refill, tea and sugar are complements to each other.
I. Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What is meant by demand?
Answer: Demand is a quantity of a commodity that a consumer wishes to purchase at a given level of price and during a specified period of time.
Question 2. Define market demand.
Answer: Market demand refers to the quantity of a commodity that all the consumers are willing and able to buy, at a particular price during a given period of time.
Question 3. Due to rise in price of commodity x the demand of commodity y falls. What type of commodity are they?
Answer: Complementary goods.
Question 4. Due to rise in price of the commodity x, the demand of commodity y also rises. What type of commodity they are?
Answer: Substitute goods.
Question 5. How will an increase in the price of petrol affect the demand curve of a car?
Answer: The demand curve of a car will shift to the left.
Question 6. A fall in the income of the consumer leads to a rise in the demand for a good. What is good X called?
Answer: Inferior good.
Question 7. What is meant by the law of demand?
Answer: It states that price of the commodity and quantity demanded are inversely related to each other when other factors remain constant (ceteris Paribus).
Question 8. When the demand for a good rises due to a fall in its own price, what is the change in demand called?
Answer: Expansion in demand.
Question 9. Define ‘change in demand’.
Answer: If demand changes due to the change in factors other than price, it is known as change in demand.
Question 10. What causes an upward movement along a demand curve of a commodity?
Answer: Rise in price of goods and fall in quantity demanded i.e., Contraction in demand.
Question 11. Give one reason for a shift in demand curve.
Answer: Change in price of substitute goods.
Question 12. What determines the quantity of a good that the buyers demand for?
Answer: The quantity of a good that the buyers demand for is determined by the price of the goods, income, the prices of related goods, tastes, expectations, and the number of buyers.
Question 13. Why market demand curve is flatter?
Answer: Market demand curve is flatter than the individual demand curves because as price falls, proportionate rise in market demand is more than proportionate rise in individual
Question 14. Ceteris Paribus, if the government provides subsidies on electricity bills, what would be the likely change in the market demand of desert coolers?
Answer: Market demand for desert coolers will Increase.
II. Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Does a rise in price of other goods have the same effect on demand for a commodity?
Answer: No, rise in prices of other goods does not have the same effect on demand for a commodity.
1. In case of rise in price of substitute goods, demand for the given commodity rises.
2. In case of rise in price of complementary goods, demand for the given commodity falls.
Question 2. Does a fall in income have the same effect on demand for the given commodity?
Answer: No, fall in income does not have the same effect on demand for the given commodity.
1. If the given commodity is a normal good, the fall in income will reduce the demand for the normal goods.
2. If the given commodity is an inferior good, the fall in income will raise the demand for the inferior goods.
3. If the given commodity is a necessity, the fall in income will not change the demand for the necessity of goods.
Question 3. What is the relation between good x and good y in each case, if with a fall in price of x demand for good y (1) rises and (2) falls? Give reason.
Answer:
1. Goods x and y are complementary goods as with fall in price of x, demand for good y rises.
2. Goods x and y are substitute goods as with the fall in price of x, demand for good y also falls.
Question 4. Giving reasons, state if the following statements are true or false:
1. An increase in the price of Coke would result in decrease in the demand for Pepsi.
2. An increase in the price of sugar would result in an increase in the demand for tea.
3. An increase in the income of a consumer would result in an increase in demand for all types of goods that are demanded by a consumer.
Answer:
1. False: Coke and Pepsi are substitute goods. An increase in the price of Coke would induce consumers to substitute Coke by Pepsi. Demand for Pepsi will increase.
2. False: Sugar and tea are complementary goods. An increase in prite of sugar would make tea costlier. Hence, the demand for tea would decrease.
3. False: With the increase in income, the consumer’s demand for normal goods will increase. Demand for inferior goods may, in fact, fall.
Question 5. Differentiate between Normal Goods and Inferior Goods.
Answer:
Question 6. Differentiate between substitute goods and complementary goods.
Answer:
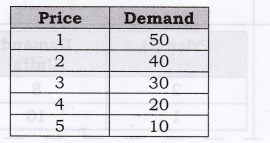
Question 7. Explain law of demand with the help of a demand schedule.
Answer:
1. It states that price of the commodity and quantity demanded are inversely related to each other, when other factors remain constant.
It means, quantity demanded of the commodity rises due to fall in price of the commodity and vice-versa.
2. Ceteris Paribus means:
(a) Price of Related commodity remains constant.
(b) Income of a consumer remains constant.
(c) Taste and preferences of a household remains constant.
3. The law of demand makes a qualitative statement only and not quantitative. It indicates the direction of change in the amount demanded and it does not indicate the magnitude of change.
4. Law of demand is one sided. It explains only the effect of change in price on the quantity demanded. It states nothing about the effect of change in quantity demanded on the price of the commodity.
Question 8. Under what conditions a consumer would like to demand more at a given level of price?
Or
State any three causes of a rightward shift of a demand curve of a commodity.
State any three factors which lead to increase in demand.
Answer: The conditions are:
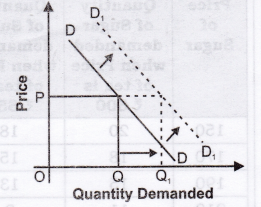
1. Price of substitute goods rises.
2. Price of complementary goods falls.
3. Income of a consumer rises in case of normal goods.
4. Income of a consumer falls in case of inferior goods.
5. When the preferences are favourable.
Question 9. Under what conditions a consumer would like to demand less at a given level of price?
Or
State any three causes of a leftward shift of a demand curve of a commodity.
State any three factors which lead to decrease in demand.
Answer: The conditions are:
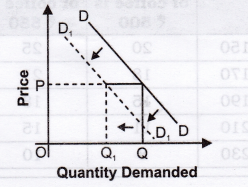
1. Price of substitute goods falls.
2. Price of complementary goods rises.
3. Income of a consumer falls in case of normal goods.
4. Income of a consumer rises in case of inferior goods.
5. When a preference becomes unfavourable.
Question 10. Differentiate between increase in demand and expansion in demand (increase in quantity demanded).
Answer:
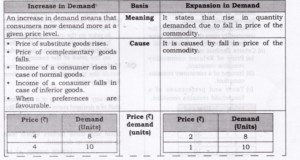
Question 11. Differentiate between decrease in demand and contraction in demand (decrease in quantity demanded).
Answer:
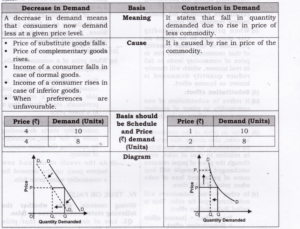
Question 12. Explain the inverse relationship between the price of a commodity and its demand.
Or
Why does law of demand slope downward from left to right?
Or
Why do household buy more at a lower price than at a higher price?
Or
Explain the causes behind law of demand.
Answer: The inverse relationship between price of the commodity and quantity demanded for that commodity is because of the following reasons:
1. Income effect:
(a) Quantity demanded of a commodity changes due to change in purchasing power (real income), caused by change in price of a commodity is called Income Effect,
(b) Any change in the price of a commodity affects the purchasing power or real income of the consumers although his money income remains the same.
(c) When price of a commodity rise more has to be spent on purchase of the same quantity of that commodity. Thus, rise in price of commodity leads to fall in real income, which will thereby reduce quantity demanded is known as Income effect.
2. Substitution effect:
(a) It refers to substitution of one commodity in place of another commodity when it becomes relatively cheaper.
(b) A rise in price of the commodity let coke, also means that price of its substitute, let pepsi, has fallen in relation to that of coke, even though the price of pepsi remains unchanged. So, people will buy more of pepsi and less of coke when price of coke rises.
(c) In other words, consumers will substitute pepsi for coke. This is called Substitution effect.
Price effect = Income effect + Substitution effect
3. Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility:
(a) This law states that when a consumer consumes more and more units of a commodity, every additional unit of a commodity gives lesser and lesser satisfaction and marginal utility decreases.
(b) The consumer consumes a commodity till marginal utility (benefit) he gets equals to the price (cost) they pay, i.e., where benefit = cost.
(c) For example, a thirsty man gets the maximum satisfaction (utility) from the first glass of water. Lesser utility from the 2nd glass of water, still lesser from the 3rd glass of water and so on. Clearly, if a consumer wants to buy more units of the commodity, he would like to do so at a lower price. Since, the utility derived from additional unit is lower.
4. Additional consumer:
(a) When price of a commodity falls, two effects are quite possible:
• New consumers, that is, consumers that were not able to afford a commodity previously, starts demanding it at a lower price.
• Old consumers of the commodity starts demanding more of the same commodity by spending the same amount of money.
(b) As the result of old and new buyers push up the demand for a commodity when price falls.
Ill. True Or False
Question 1. Law of demand states that price and demand are positively related to each other.
Answer: False: Law of demand states that price and demand are inversely related to each other.
Question 2. Law of demand happens due to application of law of diminishing marginal productivity.
Answer: False: It is due to application of law of diminishing marginal utility.
Question 3. Law of demand explains quantitative relationship between price and quantity demanded.
Answer: False: Law of demand explains qualitative relationship between price and demand.
Question 4. Change in quantity demanded means an increase and decrease in demand and Change in demand curve means expansion and contraction in demand.
Answer: False: Change in quantity demanded means expansion and contraction in demand and change in demand curve means increase and decrease in demand.
Question 5. With a fall in income, demand for normal goods will rise.
Answer: False: With a fall in income, demand for normal goods will decrease because of positive relationship between income and demand for normal goods.
Question 6. With the rise in price, quantity demanded for the goods falls and it is known as decrease in demand.
Answer: False: With a rise in price, quantity demanded falls and it is known as contraction in demand. It is not. an decrease in demand as it changes due to factors other than price.
Question 7. If price of substitute goods falls, demand for related goods will also fall?
Answer: True: With a fall in price of substitute goods, demand for its related goods will fall as there exists positive relationship between them.
Question 8. If income of the buyer decreases, demand for inferior goods decreases.
Answer: False: When income of the buyer decreases , demand for inferior goods increases. It is so because inverse relationship exists between them.
Question 9. If Indian Airlines reduce fares from Delhi to Mumbai, demand curve for air travel shifts rightward.
Answer: False: It is due to price change. It is expansion and not increase in demand.
‘