Practice questions chapter elasticity of demand microeconomics Class 11
Question
What is the Elasticity of Demand?
Ans: Elasticity of Demand refers to the percentage change in demand for a commodity with respect to the percentage change in any of the factors affecting demand for that commodity.
Question
What are the 5 Degrees of Elasticity of Demand?
Ans: 5 types of price elasticities of demand are:
- Perfectly elastic demand
- Perfectly inelastic demand
- Highly elastic demand
- Less elastic demand
- Unitary elastic demand
Question
What are the factors that affect the price elasticity of demand?
Ans: Factors affecting the price elasticity of demand are:
- Nature of commodity
- Availability of substitutes
- Income level
- Level of price
- Number of uses
- Time period
- Habits
Question
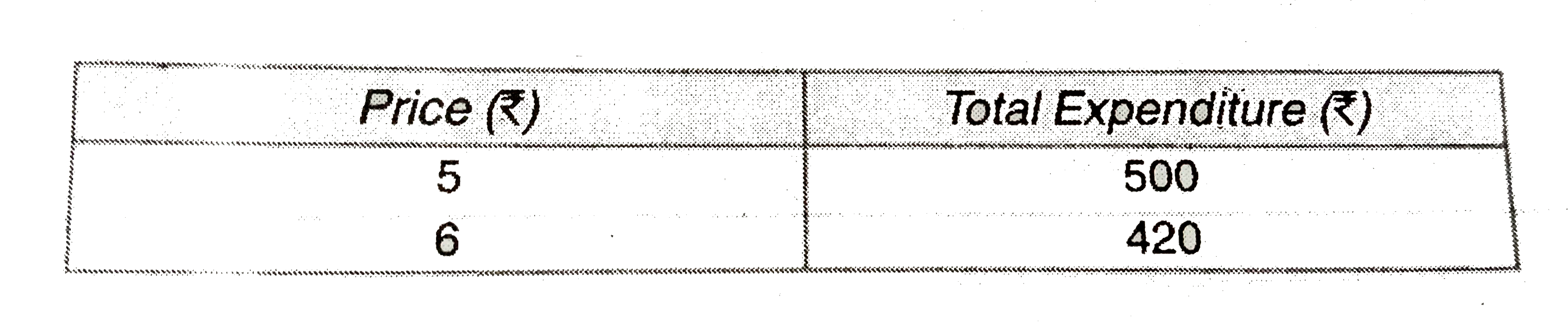
The demand for a good falls to 240 units in response to the rise in price by ₹.2. If the original demand was 300 units at the price of ₹.20, calculate the price elasticity of demand.
| New Quantity () = 240 Units | Rise in Price () = ₹2 |
| Original Quantity (Q) = 300 Units | Original Price = ₹ 20 |
| Change in Quantity () = -60 Units | New Price () = ₹ 22 |
| Elasticity of demand = ? | |
Solution:
State whether the following statements are true or false.
Question
A commodity with a large number of close substitutes shows high elasticity of demand.
Ans: True
Question
In the case of the horizontal straight line demand curve, demand does not change even with the change in price.
Ans: False
What are the 6 factors that affect demand?
The factors that affect demand are as follows:
- Price of product
- Consumer’s Income.
- Price of Related Goods.
- Tastes and Preferences of Consumers.
- Consumer’s Expectations.
- Number of Consumers in the Market.
What is the basic law of demand?
Basic law of demand states that price and quantity demanded are inversely related to each other while keeping all other factors constant. Increase in price lowers the demand for any goods or services.
What increases demand for a normal good?
Demand for normal goods increases with respect to rise or increase in consumer’s income.